DIN 84-90
Flachkopfschrauben mit Schlitz; Produktklasse A
Supersedes October 1988 edition.
In Keeping with current practice in standards published by the International Organization for standardization (ISO), a comma has been used throughout as the decimal marker.
This standard should be used together with ISO 1580, For details, see Explanatory note. It is intended to withdraw the present standard by 31 July 1995 at the latest.
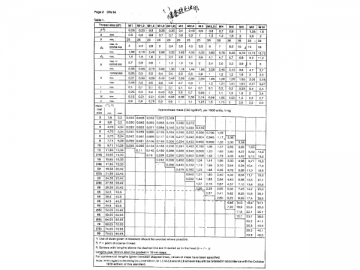
Dimensions in mm
1 Scope and field of application
This standard specifies requirements for M3 to M10 slotted pan head screws assigned to product grade A. See DIN 962(or the standards referred to therein) for special screw types and finishes. If, in special cases, screws are to comply with specifications other than those given in this standard (e.g. regarding property class or material), these shall be selected in accordance with the relevant standards.
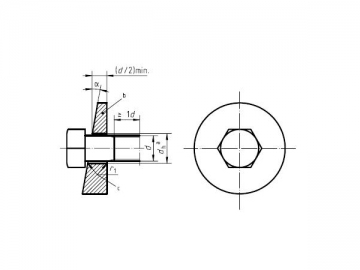
2 Dimensions
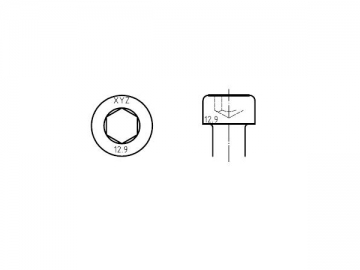
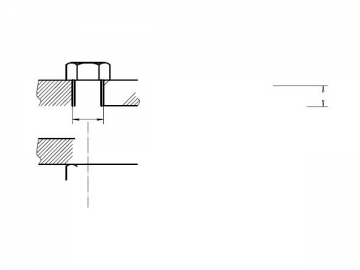
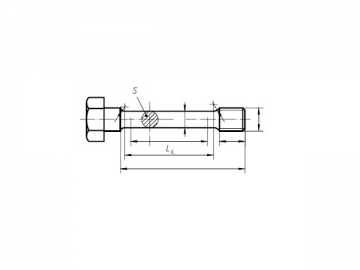
Pan head screw threaded up to the head (specified in table 1 above dashed line)
Pan head screw with unthreaded portion of shank ( specified in table 1 below dashed line)1)
Screws to be provided with DIN78-Ko end.
Other dimensions and details as at left
The shank diameter may be equal to the thread diameter (normal shank )or approximately equal to the pitch diameter(reduced shank), at the manufacturer’s discretion.
1) If pan head screws with lengths given below the dashed line are to be supplied with their shank threaded up to the head, letter A shall be given in the designation, in accordance with DIN 962.
Continued on pages 2 to 4
3 Designation
Designation of an M5 pan head screw, of length / (nominal size )=
Pan head screw DIN 85-M5×20-4.8
DIN 962 shall apply for the designation of type and finish, with additional information to be given on ordering.
DIN 6900 shall apply for screws with captive washers (screw assemblies ) and DIN 7500 Part 1 for thread rolling screws.
The DIN
Standards referred to
DIN 13 Part 13 ISO metric screw threads; series of preferred sizes for screws, bolts and nuts from
DIN 13 Part 15 ISO metric screw threads; fundamental deviations and tolerances for screw threads of
DIN 78 Thread ends and lengths of projection of bolt ends for ISO metric screw threads in accordance with DIN 13
DIN 267 Part 1 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions; general requirements
DIN 267 Part 2 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions; design and dimensional accuracy
DIN 267 Part 5 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions; acceptance inspection (modified version of ISO 3269, 1984 edition )
DIN 267 Part 9 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions; electroplated parts
DIN 267 Part 11 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions with addenda to ISO 3506; stainless and acid resistant steel components
DIN 267 Part 18 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions; nonferrous metal components
DIN 267 Part 19 Fasteners; technical delivery conditions; surface discontinuities on bolts
DIN 962 Bolts, screws, studs and nuts; designations, types and finishes
Page 4 DIN 85
DIN 4000 Part 2 Tabular layouts of article characteristics for screws and nuts
DIN 6900 Screw and washer assembles
DIN 7500 Part 1 Thread rolling screws for ISO metric threads; dimensions, requirements and testing
ISO 898 Part 1 Mechanical properties of fasteners; bolts, screws and studs
ISO 4759 Part 1 Tolerances for fasteners; bolts, screws and nuts with thread diameters from 1,6 to
Previous editions
DIN 572: 02.23; DIN 576:02.23; DIN 85:08.21, 01.37, 10.42, 12.52, 04.64, 06.70, 12.72, 10.88.
Amendments
The following amendments have been made to the October 1988 edition.
a) A note on the period of validity has been included.
b) For M3 up to M5 screws, K min values have been corrected.
c) For M3.5, M5, M8 and M10 screws, w min values have been amended.
d) The standard has been editorially revised.
Explanatory notes
Following its decision to make the specifications regarding the head of countersunk head screws to comply with those specified in ISO 7721, the responsible committee agreed to issue national standards for all existing ISO Standards on slotted and cross recessed head screws. To facilitate the changeover to the new head dimensions, an adequate transition period has been granted (cf. foreword on page 1).
The decision to adopt the ISO head was seen to be justified by the formation of CEN / TC 185, Fasteners, in 1989 since relevant European Standards dealing with such screws will be published shortly. Note that such EN Standards will be accepted only if they agree with existing ISO Standards, to avoid another transition and that the transition period mentioned on page 1 may be shorter if the EN Standards spear sooner than expected.
There are only relatively small differences for most screw types between head dimensions as specified in DIN Standards and in those in the revised ISO Standards. Thus, serious interchangeability problems would only arise in exceptional cases. The screws should be checked for interchangeability where automatic feed and bolting systems are used.
The following table, which compares the most essential head dimensions of screws as specified in ISO 1580 and the present standard, is intended to make it easier for the user to see whether screws are interchangeable.
International Patent Classification
F 16 B 35 / 06